안녕하세요. J4J입니다.
이번 포스팅은 useInfiniteQuery를 이용하여 Infinite Scroll 구현하는 방법에 대해 적어보는 시간을 가져보려고 합니다.
들어가기에 앞서 useInfiniteQuery에 대한 개념을 모르시는 분들은 [React] React Query의 useInfiniteQuery에 대해 알아보기를 참고해주세요.
Infinite Scroll 구현 방법
[React] 무한 스크롤(Infinite Scroll) 사용하기를 확인해보시면 Infinite Scroll에 대한 개념과 react query를 이용하지 않고 Infinite Scroll을 구현한 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
IntersectionObsever와 hook을 이용하여 구현을 했었는데 이번에는 useInfiniteQuery를 곁들여서 구현해보겠습니다.
useInfiniteQuery를 사용하더라도 IntersectionObserver이 필요합니다.
왜냐하면 다음 페이지의 데이터가 호출될 타이밍을 확인해야 되기 때문입니다.
결과적으로 다음과 같은 코드를 구현할 수 있었습니다.
import * as React from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
import styled from 'styled-components';
import { useInfiniteQuery } from 'react-query';
interface Iperson {
id: number;
name: string;
phone: string;
age: number;
}
const InfiniteScroll = (): JSX.Element => {
// ref
const observerRef = React.useRef<IntersectionObserver>();
const boxRef = React.useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const getPersons = () => {
const res = useInfiniteQuery(
['infinitePersons'],
({ pageParam = 0 }) => axios.get('http://localhost:8080/persons'), {
getNextPageParam: (lastPage, allPages) => {
// 다음 페이지 요청에 사용될 pageParam값 return 하기
return true; // 여기서는 pageParam을 따로 사용하지 않기 떄문에 true return
}
});
// IntersectionObserver 설정
const intersectionObserver = (entries: IntersectionObserverEntry[], io: IntersectionObserver) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
if(entry.isIntersecting) { // 관찰하고 있는 entry가 화면에 보여지는 경우
io.unobserve(entry.target); // entry 관찰 해제
res.fetchNextPage(); // 다음 페이지 데이터 요청
}
})
}
// useEffect
React.useEffect(() => {
if(observerRef.current) { // 기존에 IntersectionObserver이 있을 경우
observerRef.current.disconnect(); // 연결 해제
}
observerRef.current = new IntersectionObserver(intersectionObserver); // IntersectionObserver 새롭게 정의
boxRef.current && observerRef.current.observe(boxRef.current); // boxRef 관찰 시작
}, [res]) // res값이 변경될때마다 실행
// 로딩 중일 경우
if(res.isLoading) {
return (
<LoadingText>Loading...</LoadingText>
)
}
// 결과값이 전달되었을 경우
if(res.data) {
return (
<Person.Container>
{res.data.pages.map((page, pageIndex) => {
const persons: Iperson[] = page.data;
return (
persons.map((person, personIndex) => {
return (
<Person.Box
key={`${person.id}/${pageIndex}`}
// 가장 마지막에 있는 Box를 boxRef로 등록
ref={(persons.length * pageIndex + personIndex === res.data.pages.length * persons.length - 1) ? boxRef : null}>
<Person.Title>{person.id}.</Person.Title>
<Person.Text>{person.name}</Person.Text>
<Person.Text>({person.age})</Person.Text>
</Person.Box>
)
})
)
})}
</Person.Container>
)
}
}
return (
<Wrapper>
{getPersons()}
</Wrapper>
)
}
export default InfiniteScroll;
const Wrapper = styled.div`
max-width: 728px;
margin: 0 auto;
`;
const LoadingText = styled.h3`
text-align: center;
`;
const Person = {
Container: styled.div`
padding: 8px;
`,
Box: styled.div`
border-bottom: 2px solid olive;
`,
Title: styled.h2`
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 12px;
line-height: 48px;
`,
Text: styled.span`
margin: 0 6px;
`
}
테스트
코드를 작성하고 화면을 띄우면 다음과 같은 결과를 확인할 수 있습니다.
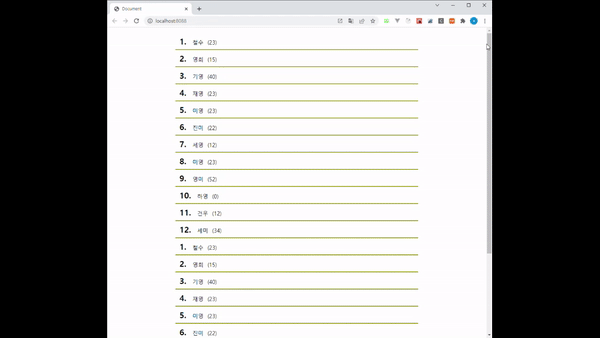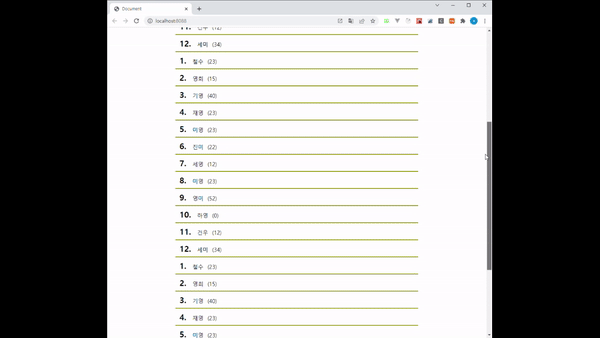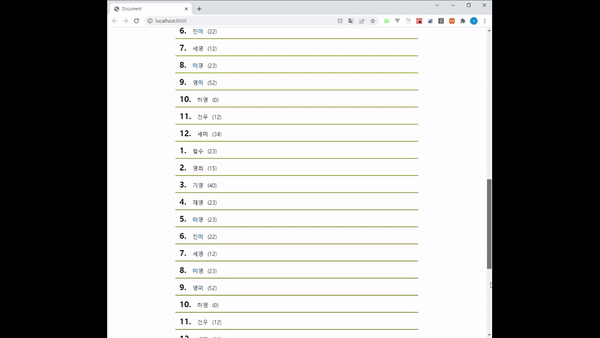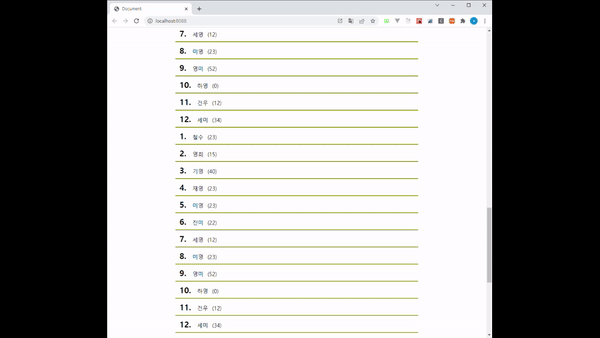
boxRef 값을 가장 마지막에 있는 Box로 잡아놨기 때문에 지금까지 호출된 데이터 중 가장 마지막에 있는 값이 화면에 보일 때마다 다음 페이지의 데이터를 호출해오고 있습니다.
그 결과로 스크롤이 점점 짧아지며 화면에 데이터가 쌓이는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
이상으로 useInfiniteQuery를 이용하여 Infinite Scroll 구현하는 방법에 대해 간단하게 알아보는 시간이었습니다.
읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
'SPA > React' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [React] 타입 스크립트(TypeScript) 환경에서 Jest를 이용하여 테스트하기 (2) | 2022.03.24 |
|---|---|
| [React] 타입 스크립트 환경에서 ESLint / Prettier 설정하기 (0) | 2022.03.21 |
| [React] React Query의 useInfiniteQuery에 대해 알아보기 (3) | 2022.03.13 |
| [React] React Query의 useQueries에 대해 알아보기 (3) | 2022.03.11 |
| [React] React Query의 useMutation에 대해 알아보기 (3) | 2022.03.09 |



댓글